Hi, this is Lizzy from Dinosaw ( Not a Robot ). Which Machine ( model ) do you want? Please WhatsApp us now
Is a stone polishing robot worth it? Understand the robotic polishing investment, ROI, and TCO for your stone factory automation in our executive guide.
TL;DR: The 30-Second Executive Overview
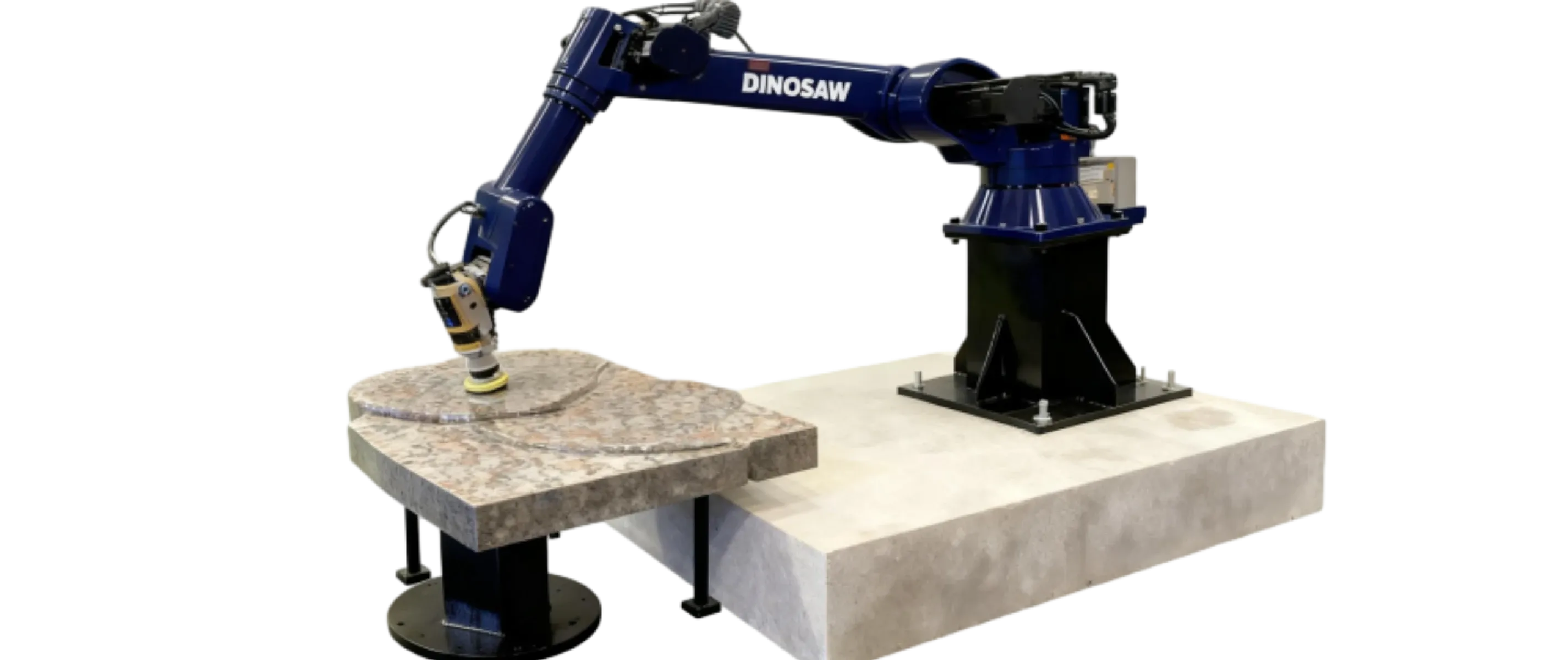
- What It Is: A robotic stone polishing system is an automated solution for finishing complex 3D surfaces like sinks, statues, and curved edges—work that is slow and inconsistent by hand.
- What It Does for You: It solves skilled labor shortages, guarantees consistent quality on high-value pieces, and enables 24/7 production, directly boosting your factory's output and profitability.
- Where It Fits: It is a strategic asset for factories producing complex, high-margin stone products. It is NOT for shops that only polish flat slabs or lack a permanent factory setup with three-phase power.
- How to Proceed: Evaluate your product mix and bottlenecks. If complex finishing is your main constraint, the next step is a formal workflow analysis to build a business case.
Frequently Asked Questions for Decision-Makers
What problem does a robot solve that other machines don't?
- Context: While a CNC line is efficient for flat surfaces, a robot's 6-axis flexibility allows it to polish inside sink bowls, around statues, and along custom edges with perfect consistency.
What is the typical robotic polishing ROI?
- Context: The ROI is driven by reduced labor costs, zero rework, increased throughput from 24/7 operation, and the ability to take on more profitable, complex jobs.
- Risk: ROI is dependent on having a consistent volume of suitable work. It is not a machine for a low-volume job shop.
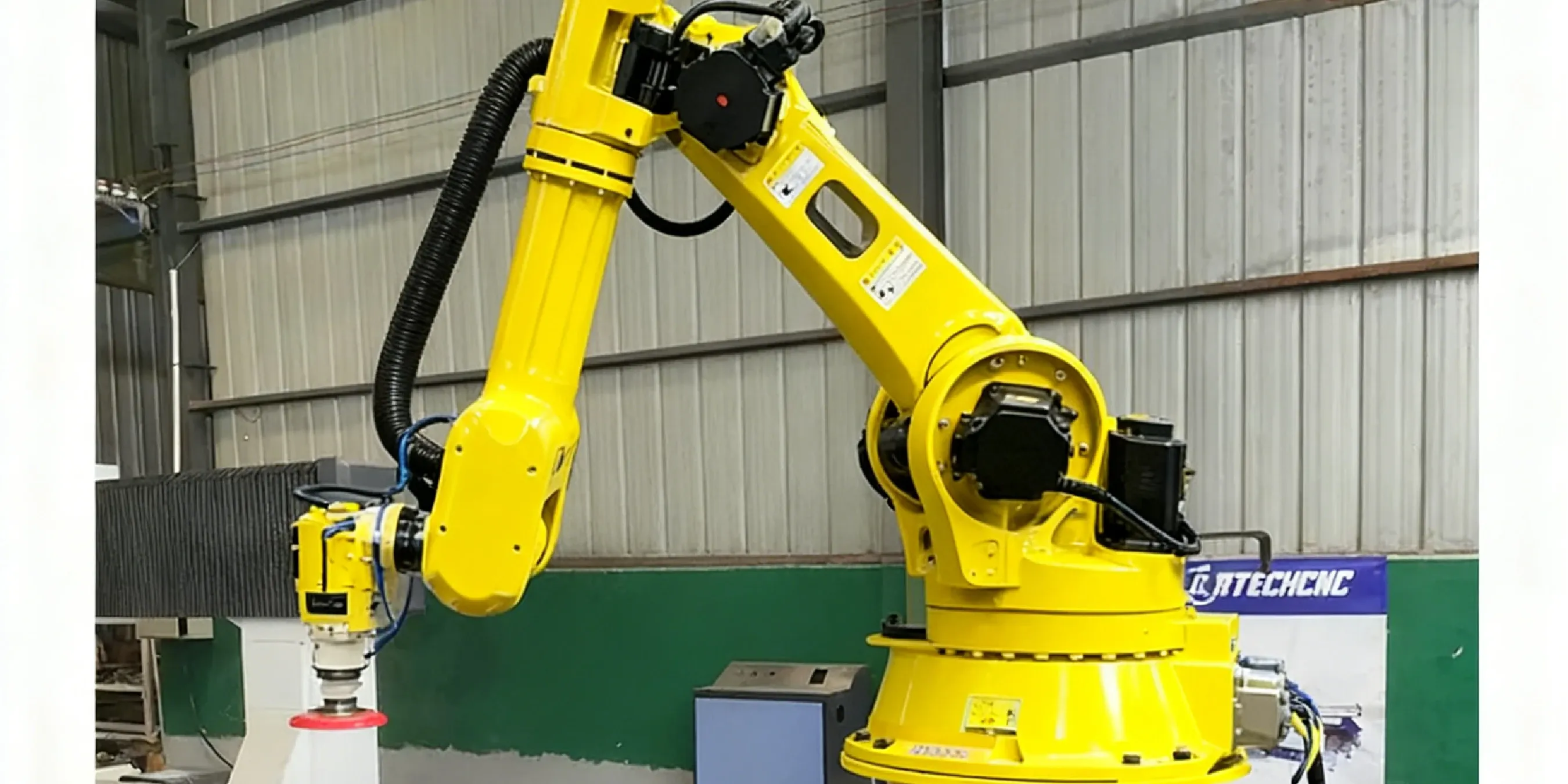 How do I justify the robotic polishing investment to my board?
How do I justify the robotic polishing investment to my board?
- Key Points: It mitigates labor shortages, guarantees quality which enhances brand reputation, and increases production capacity without expanding your factory footprint.
- Next Step: Present a formal business case including a pilot project where you test-polish your actual parts to validate quality and cycle times.
Is a polishing robot better than a skilled human?
- Context: A robot provides perfect repeatability and can work 24/7 without fatigue, making it superior for consistent output. A human artisan provides creativity and can adapt to unforeseen issues on a unique piece.
- Boundary: The goal is not to replace artisans, but to automate repetitive, physically demanding production tasks, freeing up skilled labor for higher-value work.
- Next Step: Evaluate which tasks in your workshop are "production" and which are "artistry" to identify the best fit for automation.
Are there government incentives for automation?
- Context: These can include tax credits (like Section 179 in the US), grants, or low-interest loans for capital equipment purchases. The programs vary significantly by country and region.
- Risk: These programs have strict eligibility requirements and application windows.
- Next Step: Consult with a local financial advisor or check your national/regional government's industry or commerce websites for current programs that can offset the robotic polishing machine price.
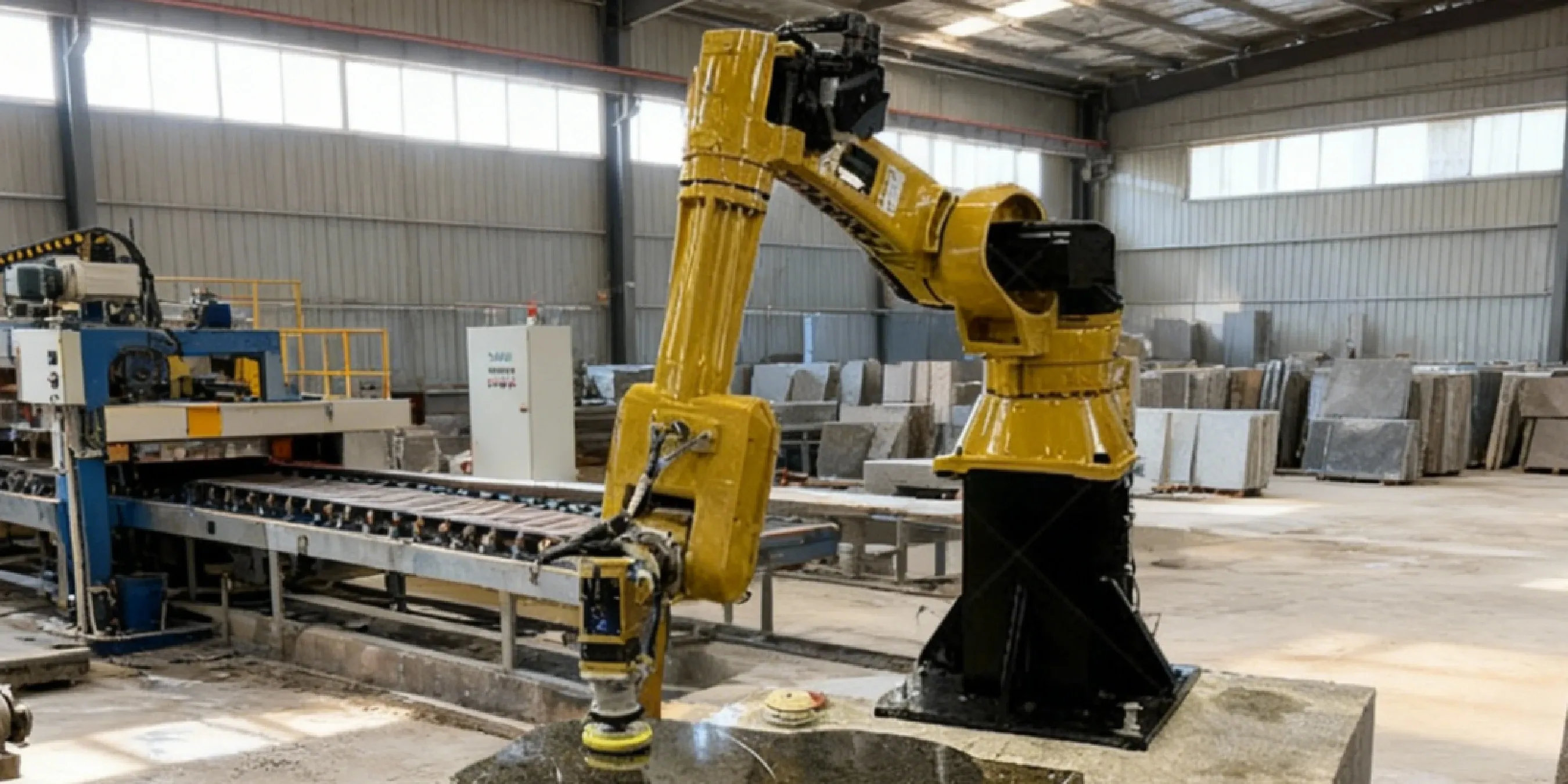 What kind of after-sales support should I expect?
What kind of after-sales support should I expect?
- Checklist: Your purchase should include:
- A detailed warranty (typically 12-24 months).
- A formal Service Level Agreement (SLA) defining support response times.
- Access to a technical support portal and remote diagnostics.
- A clear plan for spare part availability.
- Next Step: Review the after-sales support section of your contract carefully before signing. DINOSAW offers a comprehensive support package to ensure your long-term success.
What are the usage thresholds and programming requirements for polishing robots?
- Robotic Arm: Best for high-volume, low-mix production. A program is set once and runs for thousands of cycles. However, it requires a skilled programmer for each new part, creating a high usage threshold for custom work.
- CNC Polisher: Better for high-mix, varied jobs. Modern systems from manufacturers like DINOSAW have intelligent, user-friendly interfaces designed to lower the skill barrier, supported by online tutorials and engineer training (manufacturer-reported).
- Boundary: If you lack in-house programming expertise, a flexible and easy-to-use CNC is often a safer and more efficient investment.
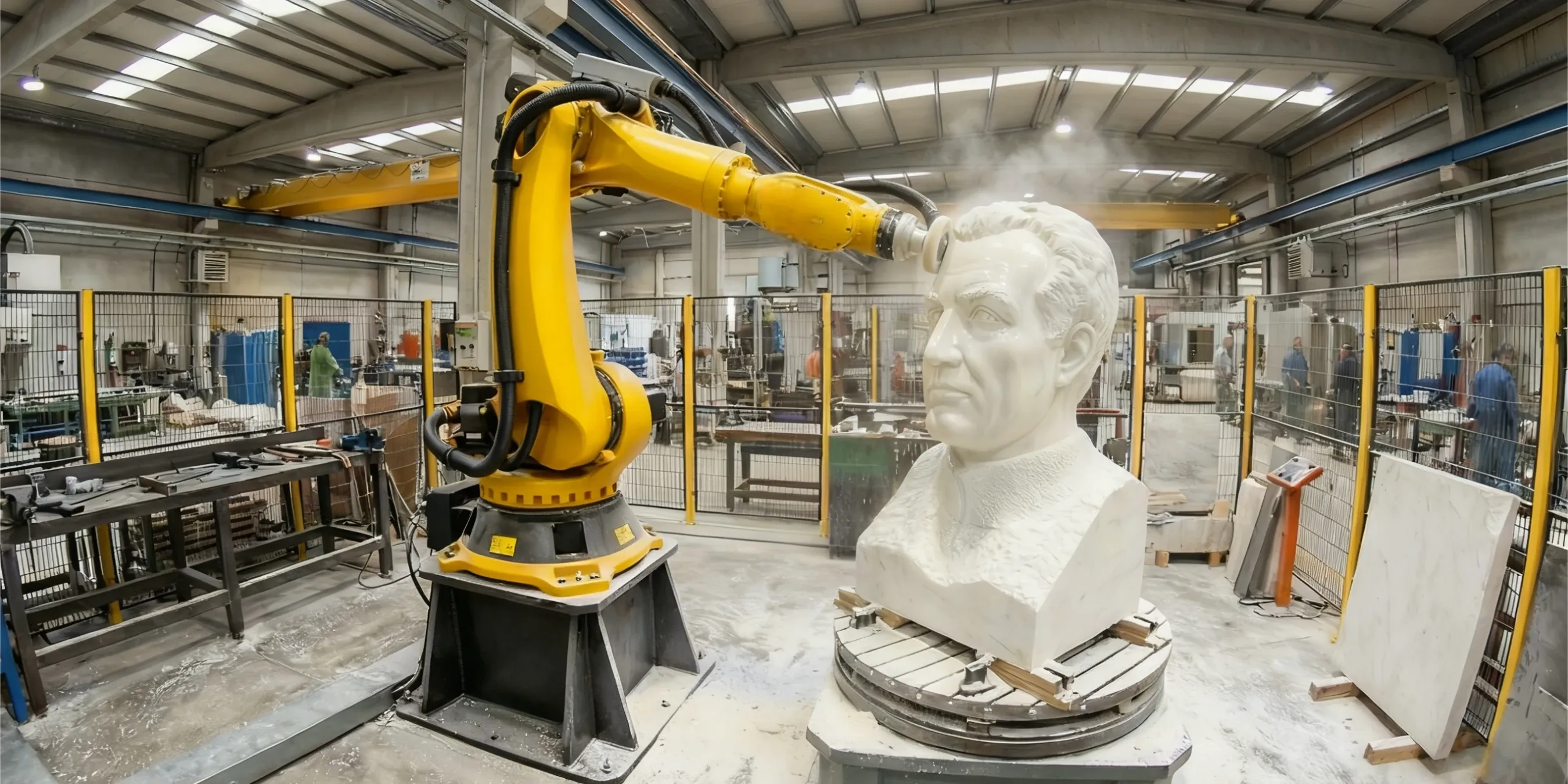

Your Robotic Polishing Investment Checklist
- Product Geometry: Do you frequently process 3D curves, integrated sinks, or complex edge profiles? (e.g., ogee, waterfall). The primary value is in non-flat surfaces.
- Materials: Do you work with granite, marble, quartz, or other stones where finish quality is a key selling point?
- Infrastructure: Do you have a dedicated factory space with a reinforced concrete floor and a three-phase industrial power supply (e.g., 380V/480V)? This is non-negotiable.
- Bottlenecks: Is manual polishing your primary production constraint? Are skilled polishers hard to find or retain?
- Safety & Compliance: Are you looking to improve workplace safety and ensure compliance with standards for silica dust exposure, such as OSHA 1926.1153?
A Phased Implementation Roadmap for Your Polishing Robot
Workflow Analysis & Goal Setting
Pilot Project & ROI Validation
Full Integration & Staff Training
Scaling & Optimization
Contract & Delivery Essentials
- Scope of Supply: Clearly itemizes every component: robot model, controller, force-control head, software licenses, and safety hardware.
- Acceptance Criteria: Defines the objective metrics (e.g., cycle time, surface gloss level) that must be met for the project to be considered complete.
- Warranty Terms: Specifies the duration and coverage for all major components. Typically 12-24 months.
- Training Package: Details the length and content of operator and maintenance training.
- Safety Compliance: The integrator must guarantee the final work cell complies with all relevant standards, such as ISO 10218-1.
- After-Sales Support: Outlines the Service Level Agreement (SLA), including response times for remote and on-site support.








 English
English 中文
中文 Italian
Italian Türkçe
Türkçe Português
Português Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch العربية
العربية Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Français
Français Русский
Русский




