Hi, this is Lizzy from Dinosaw ( Not a Robot ). Which Machine ( model ) do you want? Please WhatsApp us now
We'll break down the core components of a CNC stone engraver machine, from the spindle to the control system, and explain why it outperforms traditional methods.
TL;DR: The Engineering Breakdown
- What is it? A CNC stone engraver is a system that uses computer-controlled motors to move a cutting tool along multiple axes, carving designs from a digital file with high precision.
- Why is it better? It provides verifiable precision governed by standards like ISO 230-1 and uses closed-loop servo motors for higher accuracy and reliability than manual methods.
- What's the key takeaway? The machine's performance is a direct result of the synergy between its rigid mechanical structure and its intelligent control system.
Tech Overview: Why It's Better Than Traditional Methods
Architecture & Data Flow
[CAD Software: You create a 2D/3D design]
---> [CAM Software: Design is converted to G-code toolpaths]
---> [CNC Controller: Reads G-code and calculates motor commands]
---> [Servo Drives: Send power to motors]
---> [Motors & Ball Screws: Convert electrical signals into precise X, Y, Z motion]
---> [Spindle & Tool: Carves the stone]
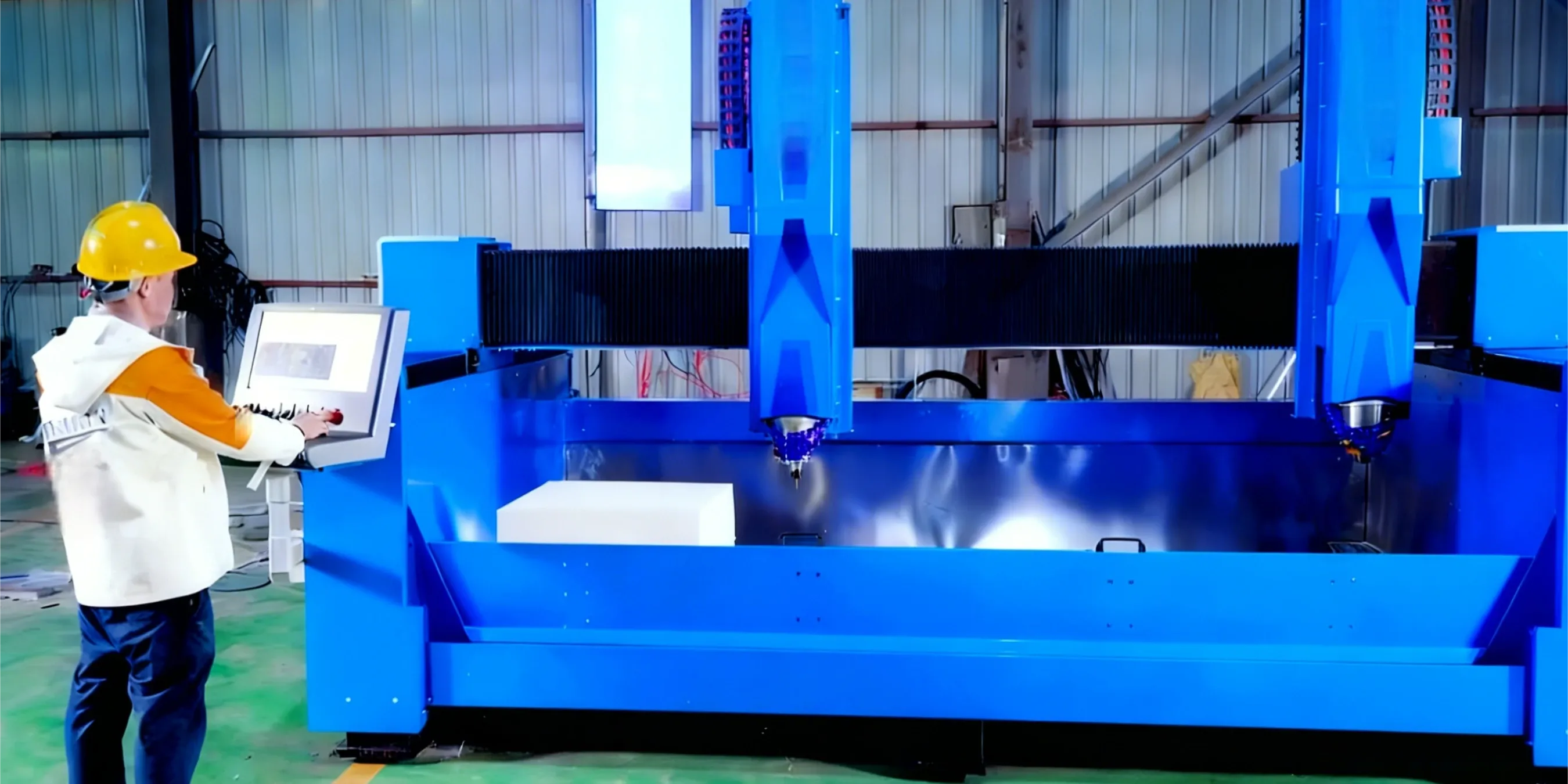 What Are the 5 Core Components That Matter Most?
What Are the 5 Core Components That Matter Most?
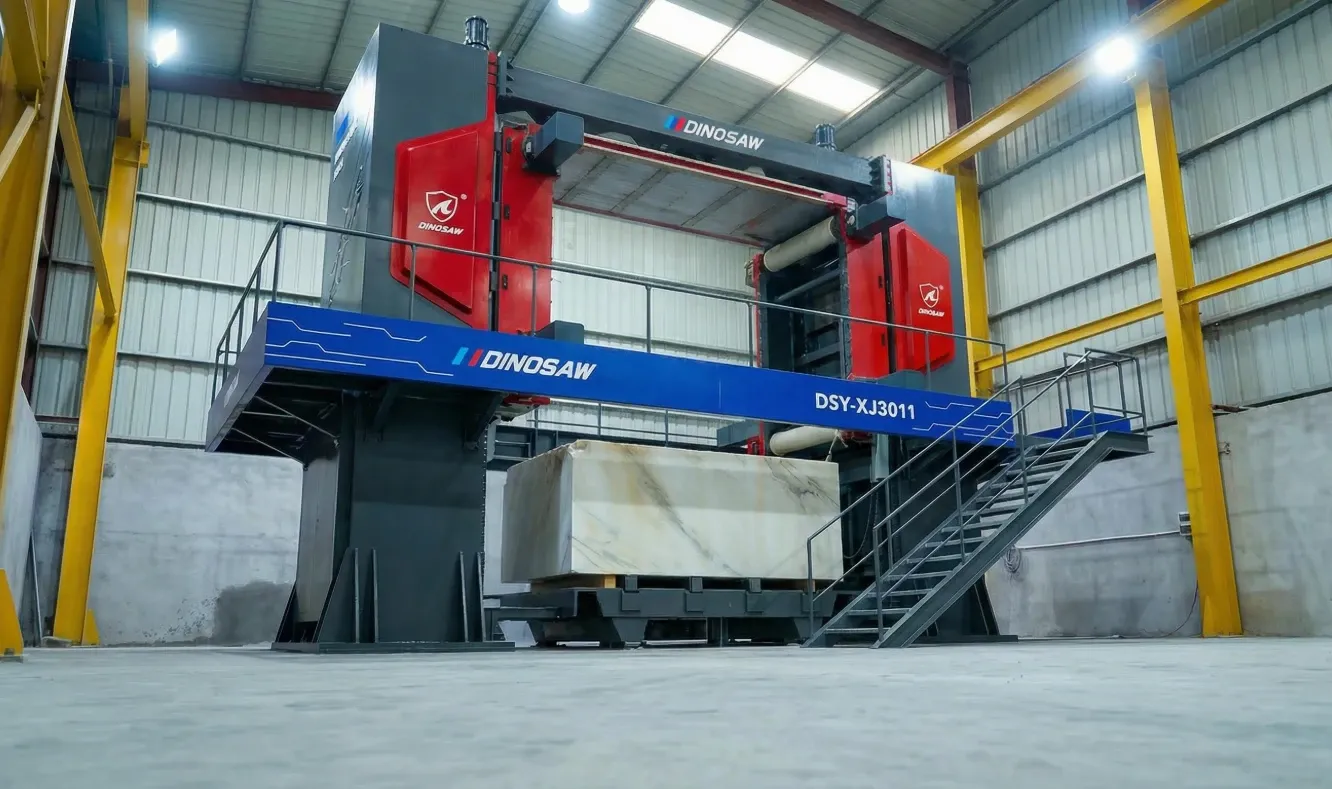
- 1. Machine Frame and Gantry: The machine's skeleton. It must be exceptionally rigid (heavy-duty, stress-relieved welded steel) to absorb vibrations. A weak frame is a recipe for inaccuracy and tool chatter.
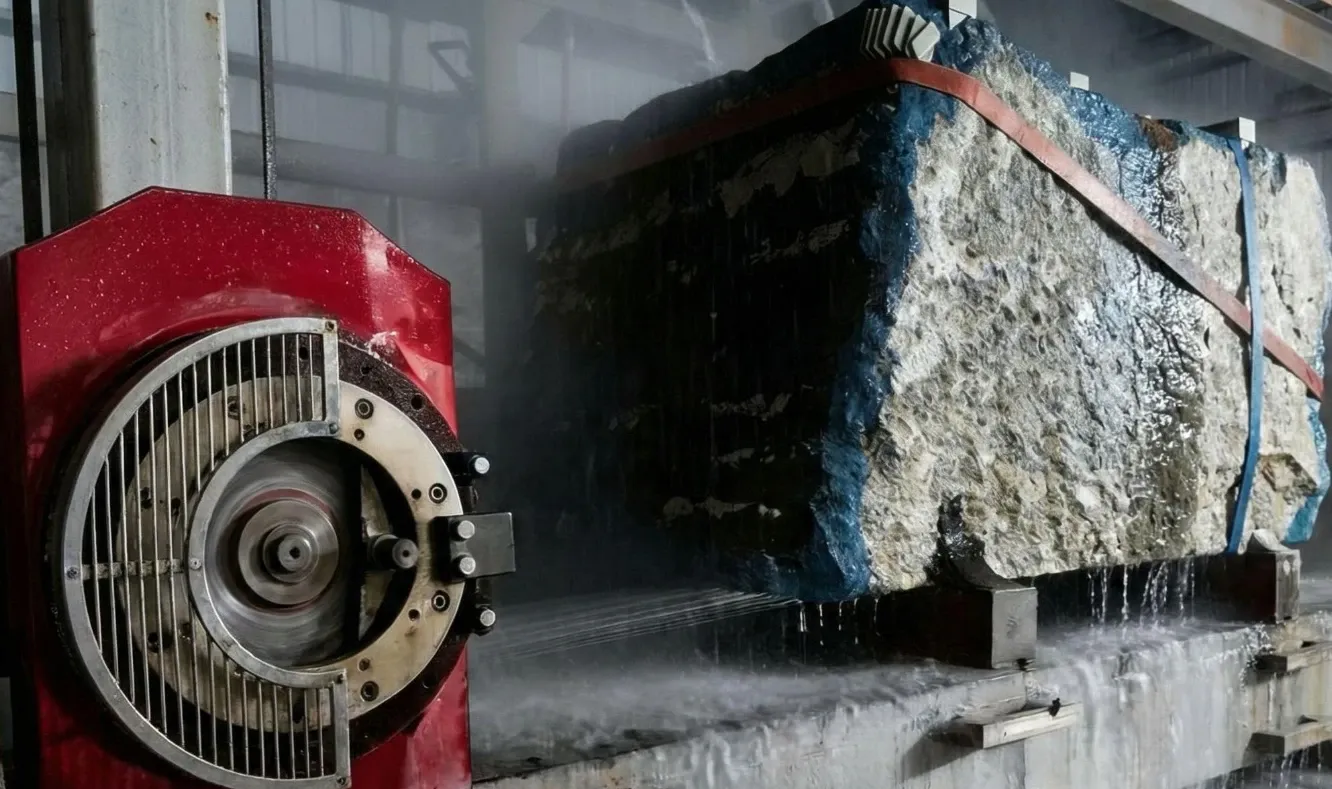
- 2. Spindle: The "heart" of the machine. For stone, a high-torque, water-cooled spindle (5.5 kW to 7.5 kW range) is essential to prevent overheating during long jobs.
- 3. Drive System (Ball Screws & Linear Guides): This translates motor rotation into precise linear motion. High-precision ball screws (compliant with standards like ISO 3408 ) ensure smooth, backlash-free movement.
- 4. Control System: The machine's "brain." Professional systems (e.g., Syntec, Siemens) offer better processing speed and "look-ahead" functions to smooth out motion.
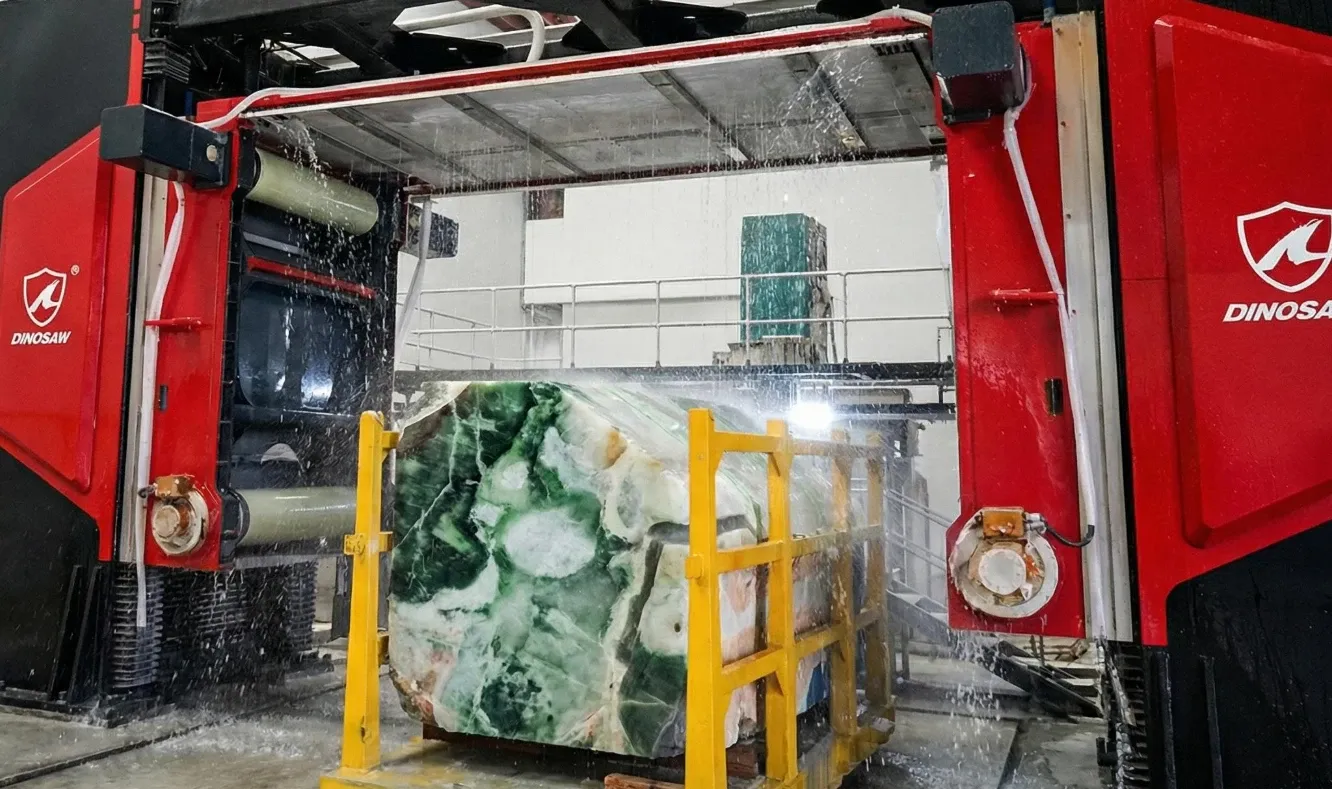
- 5. Water Cooling & Filtration: This is indispensable. It cools the CNC stone tools to prevent wear and suppresses hazardous silica dust.
Common Failure Modes & Mitigations
- Tool Chatter: Caused by a weak frame, loose workpiece, or tool stick-out. Mitigate by using a rigid machine, ensuring solid clamping, and minimizing tool length.
- Lost Steps: Occurs when stepper motors are overloaded. Mitigate by using servo motors with closed-loop feedback or by reducing cutting forces (slower feed rate, shallower cuts).
- Spindle Overheating: Caused by insufficient coolant flow or running at the wrong RPM. Mitigate by ensuring the water pump and lines are clear and operating the spindle within its specified range.
- Dust Ingress: Abrasive stone dust destroys mechanical components. Mitigate with effective seals, bellows covers on linear guides, and a positive air pressure system for electronics cabinets.
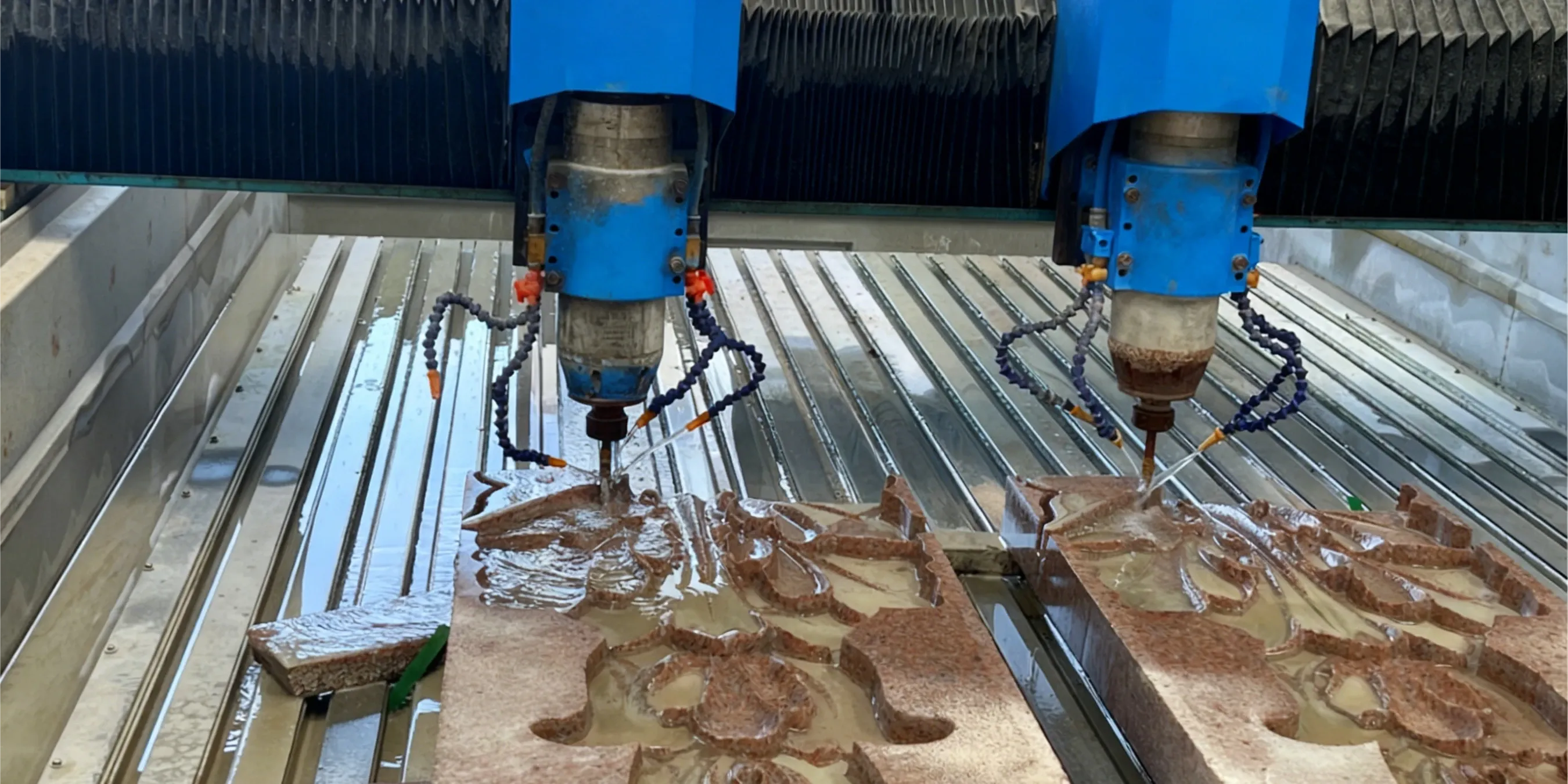 Compatibility (PLC/Interfaces)
Compatibility (PLC/Interfaces)
Three Common Scenarios: Starting Parameters
Scenario 1: Granite Bas-Relief
Scenario 2: Marble Lettering
Scenario 3: Sandstone 3D Relief
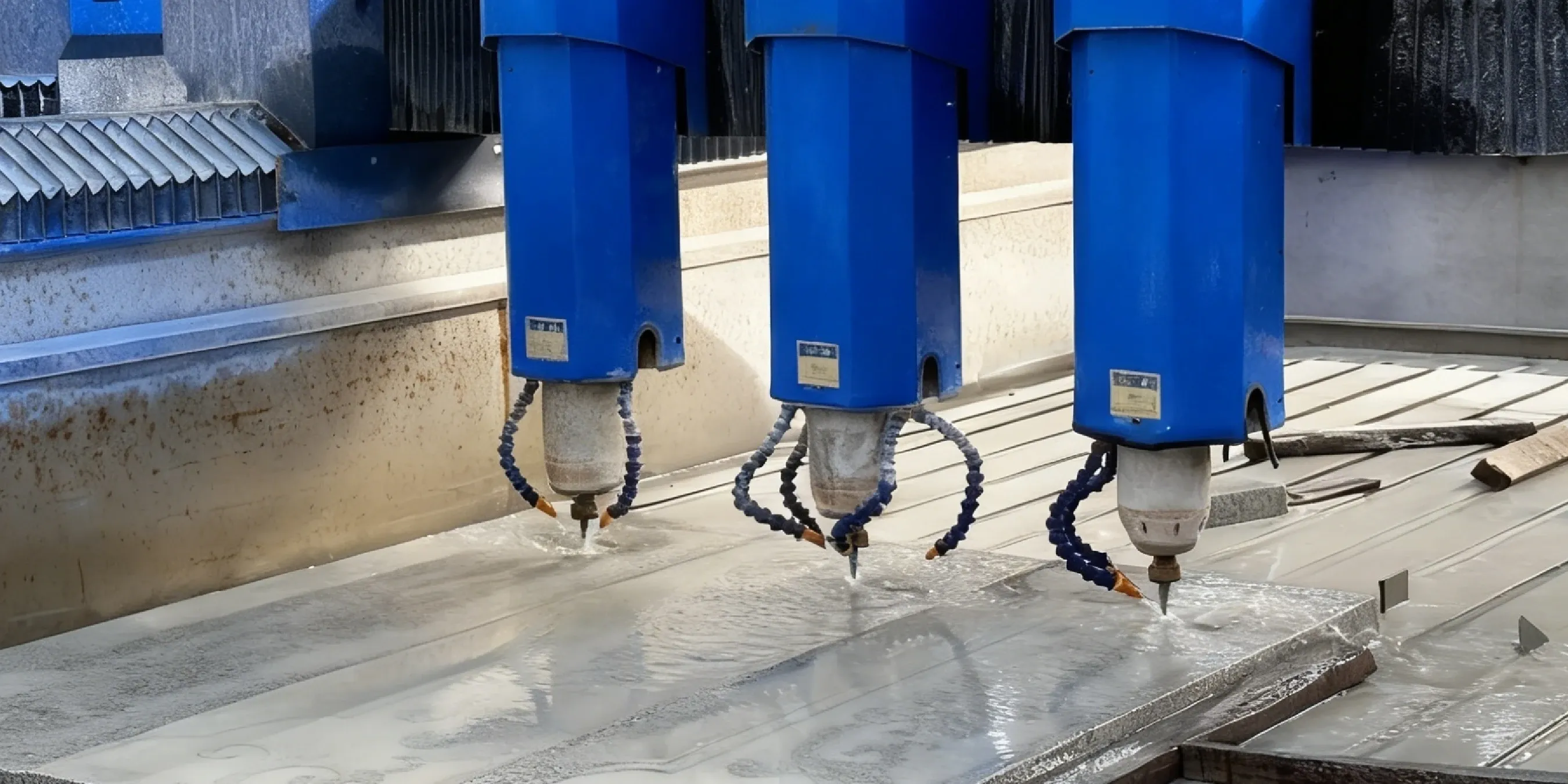 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the typical accuracy of a CNC stone engraver?
- Parameters: You can expect positional accuracy in the range of ±0.05mm to ±0.1mm. Repeatability, which is the machine's ability to return to the same spot, is often even tighter at around ±0.02mm.
- Context: This level of precision is essential for creating detailed work and ensuring uniformity across multiple pieces, which is critical when creating 3d stone engraving quotes for clients who expect consistent quality.
- Boundary: This accuracy is verified using international standards like ISO 230-1 and depends on the machine being properly installed and maintained.
What are the power requirements for this machinery?
- Parameters: A typical requirement is 380V/50-60Hz. The total power draw usually ranges from 10 kW to 15 kW, depending on the spindle size and number of axis motors.
- Risk: Assuming your workshop's power is sufficient without checking can lead to costly electrical upgrades and installation delays.
- Next Step: Always confirm the exact power requirements with the manufacturer's specification sheet before purchasing or preparing your site.
What software is compatible with your machines?
- Context: This flexibility allows you to integrate the machine into your existing design workflow without learning a new proprietary system. You can continue using software you are already familiar with.
- Examples: This includes popular programs like Vectric Aspire, ArtCAM, Type3, and Mastercam.
How do I choose the right spindle power?
- Parameters: For softer stones like marble or limestone, a 3.5–5.5 kW spindle is often sufficient. For hard stones like granite, a 5.5 kW to 7.5 kW (or higher) water-cooled spindle is strongly recommended to provide adequate torque and prevent stalling.
- Risk: Using an underpowered spindle on hard stone will lead to slow performance, poor surface finish, and can cause premature wear on the spindle itself.
What is the difference between stepper and servo motors on stone engraving routers?
- Context: Stepper motors use an "open-loop" system, meaning they can lose their position ("lose steps") if overloaded, leading to errors. Servo motors use a "closed-loop" feedback system with an encoder, allowing them to be more precise, faster, and more reliable, as they constantly verify and correct their position.
- Recommendation: For high-speed applications or precision-critical jobs, servos are always the preferred choice to ensure accuracy and avoid ruined workpieces.
What maintenance is required for the drive system?
- Context: The drive system includes the linear guides and ball screws that control the machine's movement.
- Tasks: Key tasks include lubricating these components according to a set schedule (e.g., weekly or every 40 hours of operation), keeping them clean of abrasive dust, and periodically checking for signs of wear.
- Next Step: Our O&M guide provides a detailed maintenance checklist and schedule to make this easy to manage.







 English
English 中文
中文 Italian
Italian Türkçe
Türkçe Português
Português Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch العربية
العربية Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Français
Français Русский
Русский




